Generally researchers agree that velvet antler restores, strengthens and protects normal bodily functions but is not in itself curative. Preliminary results of modern research suggest that deer velvet may have beneficial effects related to:
The concentrations of biologically active compounds and nutrients in deer antler velvet vary with different deer species and the area of the antler used. The tip of the antler is considered the most valuable in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), but the middle and base sections also offer therapeutic benefits.
Deer antler velvet has been used in TCM for over 2000 years to treat a variety of medical conditions and for preventative and restorative purposes. Research studies have demonstrated that deer antler velvet has anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-infertility, antibacterial, and antiviral properties. In addition, it has been shown to improve symptoms associated with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system, muscle strength, osteoporosis, and certain types of cancer.
The following is an overview of current research findings that support the use of deer antler velvet.
Uses of Deer Antler Velvet Base
The tip of the deer antler is typically used for most products; however, two teams of researchers have explored the uses of the base of the antler.
The antler base has already calcified making it difficult to crush and separate its bioactive components. Because of this, there is limited research regarding how the base can be used to treat health conditions.
Deer antler base has been used in TCM, and there are reports of its therapeutic effects for mammary hyperplasia, which can lead to breast cancer, mastitis, and uterine fibroids. A few researchers have analyzed the chemical components of the deer antler base and have isolated and identified amino acids, peptides, proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides as well as minerals including calcium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
In the past several decades, there have been reports on the pharmacological effects of bioactive components of deer antler base on the immune system, hematologic system, bone metabolism, glucose metabolism, cancer, fatigue, inflammation, pain, and oxidative stress.
Acute Liver Injury
Acute liver injury has numerous causes and is characterized by severe inflammation, cell death caused by oxidative stress, and necrosis of liver cells. Researchers evaluated the deer antler base to try to isolate a protein that protects mice from acute liver injury and analyze the specific mechanisms of how it protects the liver. They measured the liver enzyme levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) in serum levels along with TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels to determine the liver function and inflammation levels.
Their findings showed that the proteins extracted from the deer antler base may protect the liver from being damaged in acute liver injury through antioxidative stress and anti-inflammatory effects. The authors suggest that deer antler base protein may be a potential new drug to treat and/or prevent acute liver failure.
Conditions Affecting Bone and Muscle
Researchers in China evaluated the mechanisms by which deer antler velvet treats intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) (also known as osteoarthritis of the spine).
Osteoblasts, which are immature cells that make bone, are protected by the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of deer antler velvet. Estradiol and estrone, which are female sex hormones, are active compounds found in deer antler velvet that increase the activity of anti-inflammatory markers while reducing the secretion of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6). The data from the study showed that estrone was more effective than estradiol in slowing the progression of IVDD and may represent a potential target for drug therapy.
Strength and Endurance
A double blind study was done to determine the effects of deer antler velvet on aerobic performance, strength and endurance. The subjects were tested before supplementation and after 10 weeks. All subjects were measured for circulating levels of testosterone, insulin-like growth factor, erythropoietin, red cell mass, plasma volume, and total blood volume. Additionally, muscular strength, endurance, and VO2max were determined.
All groups improved strength equivalently, but there was a greater increase in isokinetic knee extensor strength and endurance in the group that took deer antler velvet compared to placebo group. There were no endocrine, red cell mass or VO2max changes in any group.
In another study, researchers in Korea evaluated the effectiveness of fermented deer antler velvet in increasing muscle mass and strength that is associated with aging. Fermentation has been demonstrated in several research studies to improve the way deer antler velvet functions, particularly in stimulating osteoblasts to mature and mineralize to increase bone mass. In the current study, fermented antler was tested to determine if it improves the function of skeletal muscle tissue in middle-aged mice that has been weakened by the aging process. The mice were fed a normal diet supplemented with either fermented deer antler velvet or creatine, which increases the energy supply to muscle cells and exercise performance for at least four weeks. They found that the mice that were fed fermented deer antler velvet had increased muscle mass and strength after four weeks of being on that diet. The results are promising and need to be tested on humans to determine the effectiveness of fermented deer antler velvet and its potential for being developed as a nutraceutical supplement.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition in which the bones become fragile due to a loss of bone mass and density and is frequently seen in women after they go through menopause. Estrogen, a female hormone, decreases after menopause causing increased bone resorption by osteoclasts and reduced bone formation by osteoblasts. Osteoporosis places women at risk of fractures, especially hip fractures, which can negatively impact their quality of life.
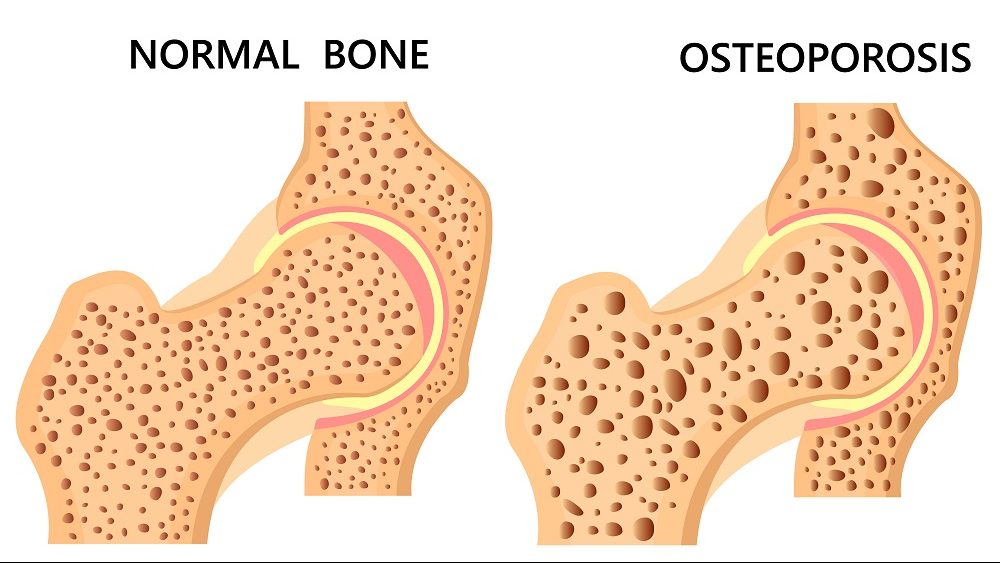
Deer antler velvet has been used to treat osteoporosis in women for years; however, its mechanism of action is unclear. A group of researchers in China used several databases (BATMAN-TCM, GeneCards, and OMIM) to find the components and targets of deer antler velvet that may be responsible for treating osteoporosis. Adenosine triphosphate, estradiol, and estrone were identified as potential mediators of cellular differentiation, apoptosis (cell death), metabolism, and inflammation.
Skin Repair
Deer antler velvet is known to contain several growth factors including insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), vascular endothelial growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor. Previous research studies have used growth factors extracted from other natural products and have shown potential in regenerative medicine for repairing injured cells, tissues, and organs.
EGF and IGF-1 play important roles in promoting epidermal and dermal regeneration as well as collagen production by fibroblasts. Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure used by plastic surgeons to remove the thicker, outer layer of skin to exfoliate and diminish signs of aging. A group of researchers in Thailand sought to develop a delivery system for microdermabrasion by using sponge spicules, which are needle-like structures, to improve skin permeation of proteins and growth factors found in deer antler velvet. They developed a cream containing broken microspicules and deer antler velvet extract, which demonstrated high skin permeability and increased elasticity and moisturization.
Brain Cancer
Glioblastoma is an aggressive form of brain cancer that is characterized by extensive infiltration of the brain and/or spinal cord but does not usually spread to other organs. If left untreated, it can lead to death in six months or less. The standard treatment is the surgical removal of the tumor which is followed by radiation therapy and chemotherapy treatment with temozolomide. Currently, these are the most effective treatments for glioblastoma, but they only extend a person’s life by about 14 months, and < 5% live longer than five years. Previous studies have shown the anti-cancer properties of deer antler velvet including the expression of several tumor suppressor genes that may prevent the rapid cell proliferation seen in most cancers. Researchers in Spain analyzed the anti-cancer effects of deer antler velvet in glioblastoma cell lines compared with temozolomide. They were able to demonstrate that deer antler velvet extract taken from the tip of the antler was more effective at inhibiting glioblastoma cell lines than samples taken from the middle of the antler. It was also non-toxic in non-cancerous cell lines. The data from this study may provide a novel therapeutic agent to further investigate as a treatment for glioblastoma.
Prostate Cancer
Researchers in Korea evaluated the effectiveness of deer antler velvet in inhibiting the migration of prostate cancer cells and preventing metastasis to other organs. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 is an enzyme that is responsible for triggering the migration of tumor cells in prostate cancer, which results in metastasis to other organs. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is thought to be the main factor that causes angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) of tumors in prostate cancer and is also associated with metastasis. Prostate cancer is diagnosed based on prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels and clinical signs and symptoms. The findings from this study demonstrated a reduction in PSA levels along with decreased migration rates of prostate cancer cells and the expression of genes associated with metastasis. Deer antler velvet also increased levels of two enzymes that are inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
For thousands of years, deer antler velvet has been thought to reduce inflammation in a variety of diseases and conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune diseases, and osteoarthritis. There have been recent reports in the past few decades that deer antler velvet also has immunomodulatory and wound-healing properties. Researchers from China used simulated gastrointestinal digestion of proteins with pepsin-pancreatin hydrolysate to evaluate deer antler velvet for peptides (short chains of amino acids) that demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects on macrophages. Although a peptide with 68 amino acids was previously isolated from Sika deer antler velvet, no other studies have tried to identify anti-inflammatory peptides from proteins found in antler velvet. After digestion of the sample of deer antler velvet protein, researchers were able to identify four peptides that had strong anti-inflammatory properties suggesting that they could be used as ingredients for nutraceuticals to combat inflammation.
Researchers in Taiwan took a different approach to investigating the anti-inflammatory properties of deer antler velvet and sought to determine if there was a difference between two different types of deer, Formosan sambar deer (Rusa unicolor swinhoei (SVAE) and red deer (Cervus elaphus (RVAE). They also examined different storage conditions and their effects on the anti-inflammatory properties of deer antler velvet extracts. The SVAE deer are indigenous to Taiwan and may represent another source of quality deer antler velvet than RVAE deer. The inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 were used to determine differences in anti-inflammatory properties. Both SVAE and RVAE significantly reduced the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 and increased the production of IL-10 (an anti-inflammatory cytokine; however, SVAE had stronger responses. The extracts were stored in temperatures ranging from -20 C to 25 C for six months. The anti-inflammatory effects of SVAE decreased as the storage duration increased, but the different temperatures did not have any significant effects.
Summary
Even though deer antler velvet and deer antler base have been used in TCM for thousands of years, researchers are still discovering components of both that are effective in treating or preventing numerous diseases/conditions.
As advancements are made in technology, drug development, and research techniques, researchers will have more tools at their disposal to analyze deer antler velvet and deer antler base. The goal is to gain a better understanding of its bioactive components so that the future discovery of new medications and nutraceuticals will be possible.

